| A quadrilateral is a 2-dimensional closed shape with four straight
sides. E.g. The shape ABCD shown here is a quadrilateral.
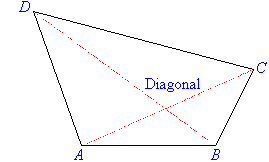
A line segment drawn from one vertex of a quadrilateral to the opposite
vertex is called a diagonal of the quadrilateral. AC is a
diagonal of quadrilateral ABCD, as is BD.
Types of Quadrilaterals
There are seven types of quadrilaterals that can be divided into two
groups: parallelograms and other quadrilaterals.
Parallelograms
Quadrilaterals are called parallelograms if both pairs of opposite sides
are equal and parallel to each other. Different parallelograms and
their properties are described below.
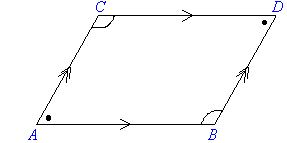
Parallelogram
- Opposite sides of a parallelogram are parallel and equal in length.
- Opposite angles are equal in size.
Note:

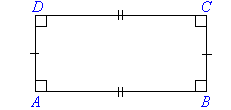
Rectangle
- Opposite sides of a rectangle are parallel and equal in length.
- All angles are equal to 90°.
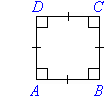
Square
- Opposite sides of a square are parallel and all sides are equal in
length.
- All angles are equal to 90°.
Rhombus
- All sides of a rhombus are equal in length
- Opposite sides are parallel.
- Opposite angles of a rhombus are equal.
- The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles.
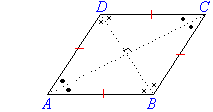
Note:
Rectangles, squares and rhombuses (or diamonds) are parallelograms.
Other Quadrilaterals
Other quadrilaterals include trapeziums, kites and irregular
quadrilaterals.
Trapezium
- A trapezium has one pair of opposite sides parallel.
- A regular trapezium has non-parallel sides equal and its base angles
are equal, as shown in the diagram.

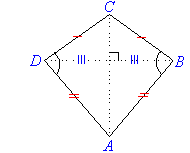
Kite
- Two pairs of adjacent sides of a kite are equal in length
- One pair of opposite angles (the ones that are between the sides of
unequal length) are equal in size.
- One diagonal bisects the other.
- Diagonals intersect at right angles.
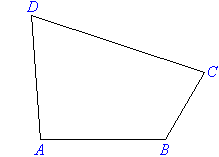
Irregular Quadrilateral
An irregular quadrilateral does not have any special properties.
Angle Sum of a Quadrilateral
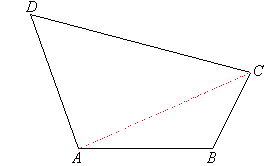
Draw a quadrilateral ABCD. Then draw the diagonal AC to form two triangles.
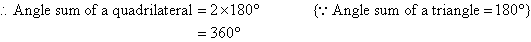
Finding the Fourth Angle of a Quadrilateral
If the measurements of three angles of a quadrilateral are known, then
the missing angle can be calculated.
Example 21
Find the value of the pronumeral x in the accompanying
diagram. Give reasons for your answer.
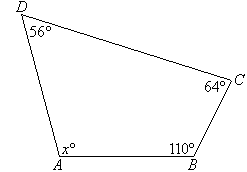
Solution:
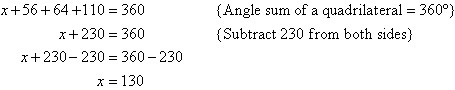
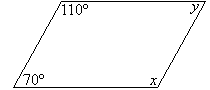
Example 22
Find the value of the pronumerals in the following diagram. Give
reasons for your answer.
Solution:
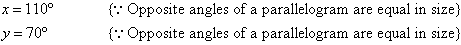
Example 23
Find the value of the pronumerals in the following diagram. Give
reasons for your answer.
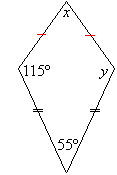
Solution:

Key Terms
quadrilateral, diagonal of a
quadrilateral, parallelogram, rectangle, square, rhombus, trapezium, kite, irregular quadrilateral, angle
sum of a quadrilateral |