Subtracting one number from another number is to find the difference
between them.
The symbol used for subtraction is '–'. This is known as the minus
sign.
For example, 14 – 6 = 8
This is read as fourteen take away six is equal to eight (or fourteen
take away six is eight). Also, we can say that 14 minus 6 is 8.
Example 6
Subtract 8 from 17.
Solution:
17 – 8 = 9
Subtraction of Large Numbers
To subtract large numbers, list them in columns and then subtract only
those digits that have the same place value, as illustrated below.
Example 7
Find the difference between 8053 and 397.
Solution:
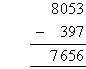
Note:
- We could calculate the above subtraction using the equals addition method.
This method adds the same number (10, 100, 1000 etc.) to both the top
number and the bottom number but in different columns whenever the top
number's place value cannot be subtracted from the bottom number's place
value. This is shown for Example 7 in the following three steps.
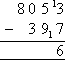 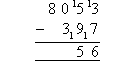 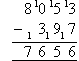
- As 7 cannot be subtracted from 3, add 10 units to 3 in the top number
to form 13 and add 10 units to 90 in the bottom number which adds up to
100 as shown above. The answer remains the same because we have added 10 to
the both the top number and bottom number. We can now subtract 7
from 13 to obtain 6 in the units column.
- Continuing on, 5 tens (in the tens column) is smaller than 10 tens
(9 + 1 tens). So, we need to add 10 to 5 in the tens column and add 1 to 3 in the
hundreds column. The answer remains the same because we have just
added 100 to the both the top number and bottom number. We can now subtract
10 from 15 to obtain 5 as shown above.
- Finally, 0 hundreds (in the hundreds column) is smaller than 4 hundreds
(3 + 1 hundreds). So, we need to add 10 to 0 in the hundreds
column and add 1 to the thousands column of the bottom number. The answer remains the same
because we have just added 1000 to both the top number and bottom
number. We can now subtract 4 from 10 in the hundreds column and
then 1 from 8 in the thousands column as shown above.
- We could also calculate the subtraction using the decomposition method.
This method involves borrowing an amount from a higher place value and
giving it to a lower place value in the top number and re-writing the
top number so that its value does not change as shown in the following
two steps.
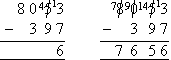
- As 7 cannot be subtracted from 3, borrow ten from the tens column and
add it to 3 and at the same time, reduce the number of tens from 5 to 4
as shown above. Now subtract 7 from 13 to obtain 6 in the units
column.
- We cannot subtract 9 from 4 in the tens column. So we must
borrow 100 from the thousands column and add it to the tens column (i.e.
add 10 to 4 to obtain 14) as shown above. You can also see that we
have reduced 8000 to 7900. Now subtract 9 from 14, 3 from 9 and 0
from 7 to complete the subtraction.
Key Terms
subtraction, subtracting,
difference, minus
sign, equals addition method, decomposition
method
|